
UNIVERSIDAD AUTÓNOMA DE NUEVO LEÓN
SECRETARÍA DE SUSTENTABILIDAD
January 26: World Environmental Education Day
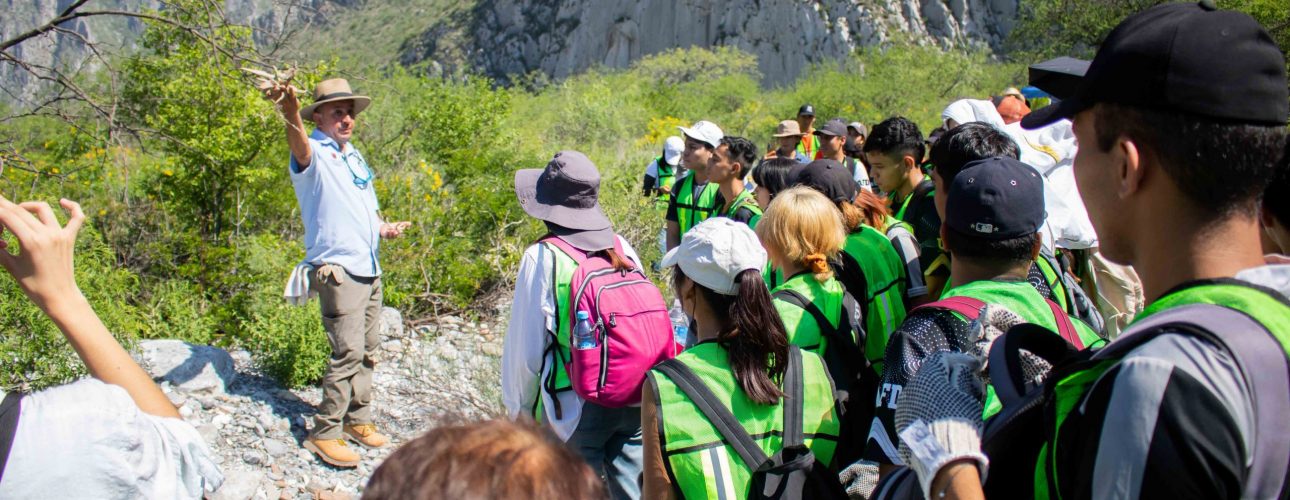

The unsustainable productive activities practiced by humanity have been the main causes of alterations to the environment, generating a series of problems such as pollution, global warming, variations in the structure and functioning of ecosystems, the extinction of species, the loss of biodiversity, among others. Due to this situation, for some decades now, actions have been promoted that contribute to conserving the environment and/or restoring those ecosystems that have been damaged.
In this context, environmental education emerged as a permanent process aimed at the formation of citizens committed to the prevention and solution of problems that affect nature, in order to establish a harmonious interaction between human societies and their environment. One of the main goals of this type of education is to develop environmental awareness among the human inhabitants of the planet, which will allow us to build an inclusive, equitable, safe and sustainable world in the near future.

In the history of the emergence of Environmental Education, the Stockholm Conference, held in Sweden in 1972, is considered a key event, because it was here where the emergence of environmental education worldwide was first proposed. leading to the publication in 1975 of one of the most important documents in this matter: the “Belgrade Charter” which contains a series of guidelines within which is the creation of healthy interactions between people and their environment, as well as between the same individuals. In addition, starting this year the celebration of World Environmental Education Day was established (Government of Chile, 2024 and Secretariat of the Environment and Natural Resources, 2021).

Environmental Education has resorted to various pedagogical strategies that range from traditional aspects to the development of skills, but always prioritizing the practical aspect where the student and the teacher in natural spaces make use of the knowledge, skills and attitudes that contribute to the care of their surroundings. In addition, it has managed to join organizations with both formal and non-formal educational purposes, companies, media, civil associations, homes, among others (Nay and Febres, 2019).
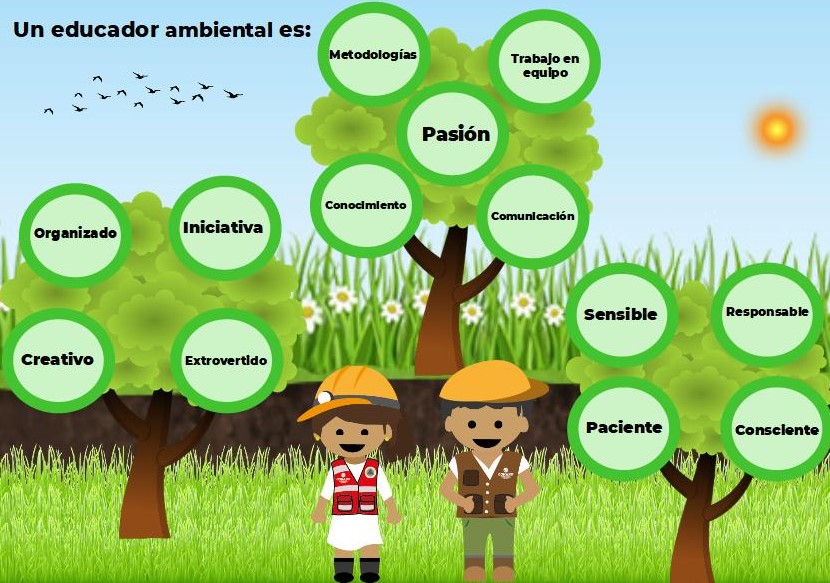
For his part, the environmental educator is a fundamental actor in the process of changing vision towards caring for the environment. They have a multidisciplinary profile and make their skills, abilities and knowledge available so that the other can develop their own criteria in addition to assuming responsibility. responsibility in the construction of its environment (National Commission of Protected Natural Areas, 2021). According to Coutiño (2015), it is defined by three aspects: an academic profile related to the environment, being proactive, and a commitment to include in one's own life what one transmits to others.
Currently, at the national level they seek to develop environmental education programs in basic, high school and higher educational institutions, through an agreement that was signed on April 26, 2021 and is valid until 2024. What is sought is to incorporate the environmental dimension to the study plans and programs, as well as the training and training of teachers on the topics that environmental education addresses, in addition to developing a design and evaluation of school environmental management models and thanks to this providing an exchange and technical assistance for the preparation of said contents and instruments (Secretary of the Environment and Natural Resources, 2021).

The Autonomous University of Nuevo León (UANL) has distinguished itself for being a Higher Education Institution committed to caring for the environment, which has led it to carry out different actions in favor of the environment, such as including the issue of care and conservation of ecosystems. in learning units, undergraduate and postgraduate programs, as well as the training of researchers and development of projects related to the preservation of the planet, integration of environmental aspects in university management, among others.
With the creation of the Sustainability Secretariat (SS) in 2010, the UANL sought to give greater impetus to environmental care and conservation actions and the promotion of sustainability in university environments and society.
Currently, the UANL Sustainability Secretariat carries out important actions in environmental education such as those described below: one of the key areas is non-formal education, which throughout the year considering the global environmental agenda proposed by the United Nations Unidas offers a series of conferences, workshops, seminars, courses, among others; where the international course on “Training leaders who promote sustainability” stands out for its importance, which since 2015 has established itself as one of the means of training leaders who promote care for the environment inside and outside university environments; In this same sense, through the non-formal education program for sustainability through social networks and the UANL Sustentable website, virtual learning objects are generated that are available to the entire public through the website and social networks. administered by the UANL Sustainability Secretariat, where issues related to environmental conservation are addressed.
In this context, the work with the university community committed to the environment has allowed us to offer a series of monthly virtual conferences, as is the case of the Permanent Seminars of the University Academy for Sustainable Development, with the participation of professors-researchers from the UANL and the online conference cycle, an event by young people for young people, with the participation of leaders who are members of UANL student associations, creating work networks for the conservation of the planet.
On the other hand, resorting to the strategy of learning laboratories since 2016, they have carried out the “Days for the recovery of natural environments in urban areas”, promoting the participation of the university community, government, civil associations, companies, civil society, among others; in order to recover public spaces with ecological importance to improve the environmental quality of urban areas, which can also be used as areas of social coexistence and recreation.
These are some of the actions carried out by the Secretariat of Sustainability in the field of environmental education and that, together with what the academic departments work on, strengthen the work of the UANL in this matter. To learn more about these activities, we invite you to know the UANL Annual Sustainability Report available at: https://sds.uanl.mx/reportes-de-sustentabilidad/
Anyone can become an environmental educator if they wish. Below, we share a series of useful tips that you can incorporate into your life, and that by practicing them little by little you will be able to acquire knowledge and experience in environmental education:
- Avoid using the car
- Make efficient use of energy
- Avoid burning wood or paper
- Be a responsible consumer
- Create a garden at home
- plant a tree
- Take care of the water
- Reduce, reuse and recycle
- Learn about circular economy
Don't leave it until tomorrow to become an agent of change towards Sustainable Development!
References:
Comisión Nacional de Áreas Naturales Protegidas. (2021). Formadores de conciencia ambiental. https://www.gob.mx/conanp/es/articulos/formadores-de-conciencia-ambiental?idiom=es
Coutiño, Julio. (2015). Tres aspectos que definen a un educador ambiental. Revista UNED, Biocenosis, 30. Pp. 1-2.
Gobierno de Chile. (2024). ¿Qué es educación ambiental? https://educacion.mma.gob.cl/que-es-educacion-ambiental/
Nay, María y Febres, María. (2019). Educación Ambiental y Educación para la Sostenibilidad: historia, fundamentos y tendencias. Encuentros, 17(2), pp. 24-45.
Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. (2018). Compendio de Estadísticas Ambientales 2018. Gobierno de México
Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. (2008). Compendio de Estadísticas Ambientales 2018. Gobierno de México. https://apps1.semarnat.gob.mx:8443/dgeia/compendio_2018/dgeiawf.semarnat.gob.mx_8080/ibi_apps/WFServleta7ab.html
Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. (2021). Convenio de colaboración Semarnat-SEP. https://www.gob.mx/semarnat%7Ceducacionambiental/articulos/convenio-de-colaboracion-semarnat-sep?idiom=es
Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. (2021). La Carta de Belgrado. https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/educacionambiental/documentos/la-carta-de-belgrado