Sustainable mobility
Sustainable mobility
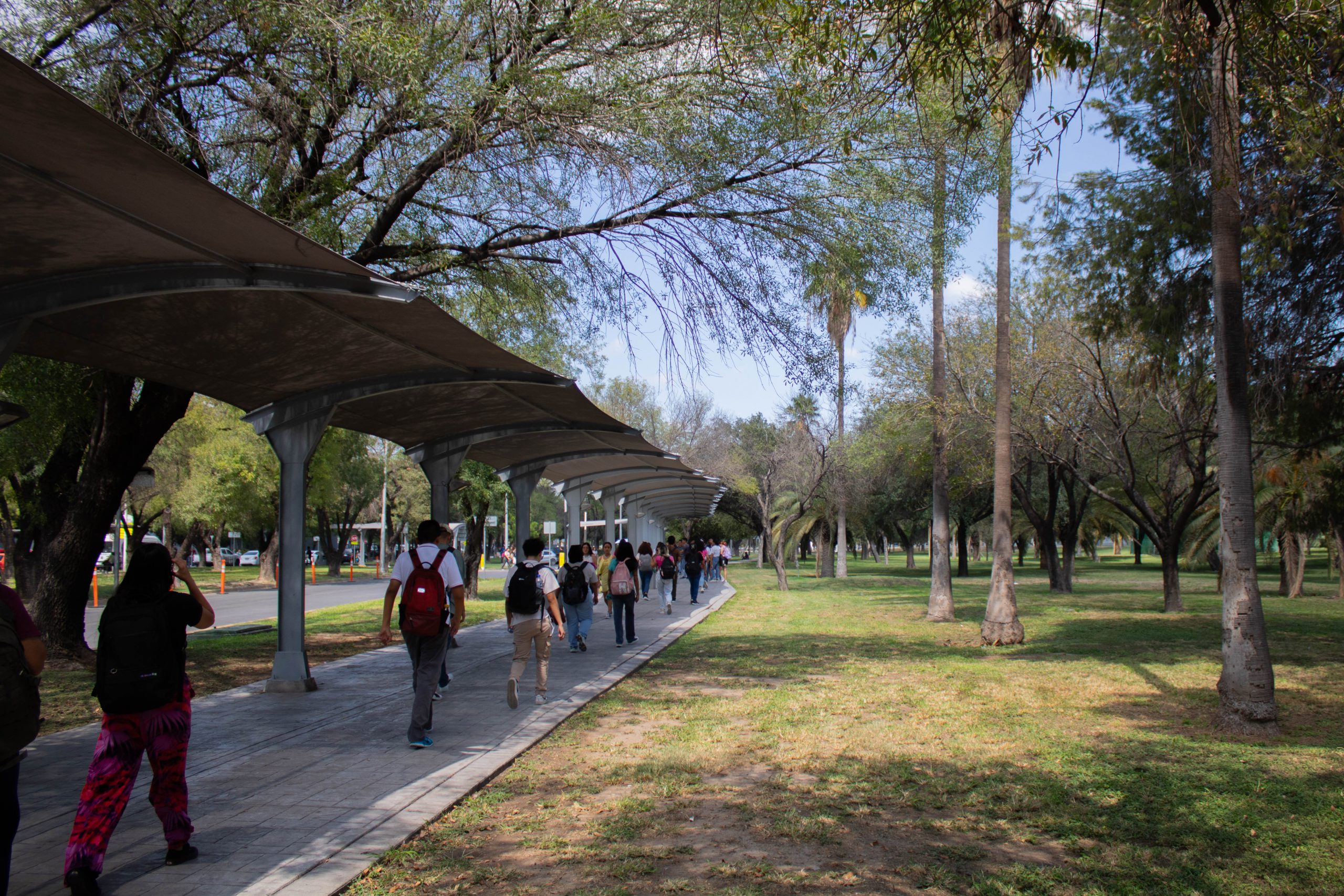

La Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León (UANL), en concordancia con sus políticas de desarrollo institucional y sustentabilidad, ha implementado un programa integral de movilidad sustentable en sus campus urbanos localizados en la Zona Metropolitana de Monterrey (ZMM). Dicho programa responde a la necesidad de disminuir la dependencia del transporte privado, promover alternativas colectivas, eléctricas y no motorizadas, así como generar una cultura de movilidad responsable entre la comunidad universitaria. Estas acciones se inscriben en un contexto metropolitano caracterizado por altos niveles de contaminación atmosférica y problemas de congestión vial ocasionados por el gran número de vehículos automotores que diariamente circulan por calles y avenidas de la ciudad.
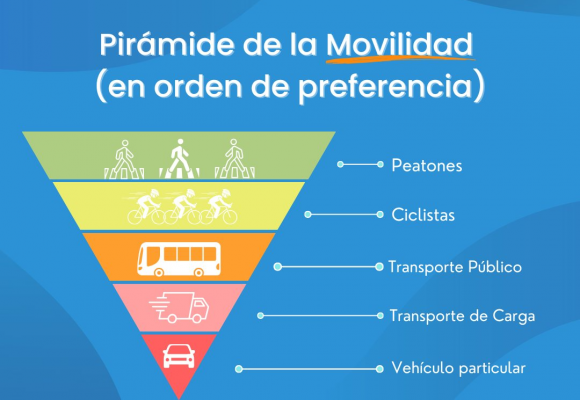
La Pirámide Invertida de la Movilidad
En la concepción de este programa, la UANL toma como referente los principios del Instituto de Políticas para el Transporte y Desarrollo (ITDP), particularmente el modelo de la Pirámide Invertida de la Movilidad. Este instrumento plantea una jerarquización del espacio que prioriza en primer lugar a los peatones, seguido por los sistemas de movilidad no motorizada, el transporte público y, finalmente, los vehículos privados en el último nivel de relevancia. Bajo esta perspectiva, el derecho al libre tránsito peatonal debe ser universal y, en consecuencia, se requiere otorgar prioridad en el diseño de accesos, vialidades y espacios de desplazamiento dentro de los campus.


Movilidad, inclusión y desarrollo institucional
La movilidad sustentable es también un factor de accesibilidad e inclusión social. De acuerdo con la Agenda de la ONU-Hábitat 2016, las ciudades deben garantizar condiciones que promuevan igualdad de oportunidades, acceso a servicios básicos y fortalecimiento del tejido social mediante la movilidad equitativa. La UANL incorpora estos principios en su Plan de Desarrollo Institucional, donde se establece la necesidad de impulsar entornos universitarios sustentables, con infraestructura adecuada y políticas que favorezcan la movilidad colectiva y no motorizada.



Beneficios ambientales y sociales
El impacto positivo del programa de movilidad sustentable de la UANL se refleja en múltiples dimensiones. En términos ambientales, contribuye a disminuir la emisión de gases de efecto invernadero y de partículas contaminantes asociadas al uso intensivo de vehículos particulares. Socialmente, garantiza igualdad de acceso a medios de transporte, promueve hábitos de vida más saludables mediante la movilidad activa y fomenta la construcción de comunidades universitarias más cohesionadas e incluyentes. Económicamente, reduce los costos individuales de traslado y genera ahorros colectivos al disminuir la presión sobre la infraestructura vial.
El caso de Ciudad Universitaria
Dentro de los campus de la UANL, Ciudad Universitaria representa un espacio prioritario de intervención, debido al alto porcentaje de población que diariamente se traslada hacia y desde sus instalaciones. En este contexto, la movilidad no motorizada adquiere relevancia estratégica, al permitir desplazamientos internos más seguros, accesibles y sustentables. Apostar por este modelo implica beneficios ambientales directos, como la reducción de emisiones contaminantes, pero también sociales, al reforzar el tejido comunitario mediante la creación de espacios públicos adecuados, áreas de convivencia y corredores peatonales que fortalecen la cohesión social.
Ejes de acción del programa
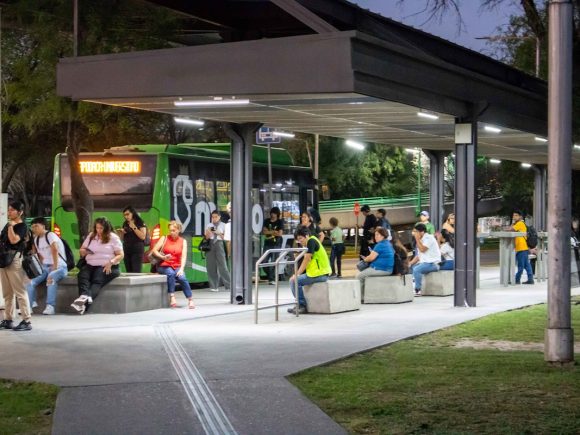
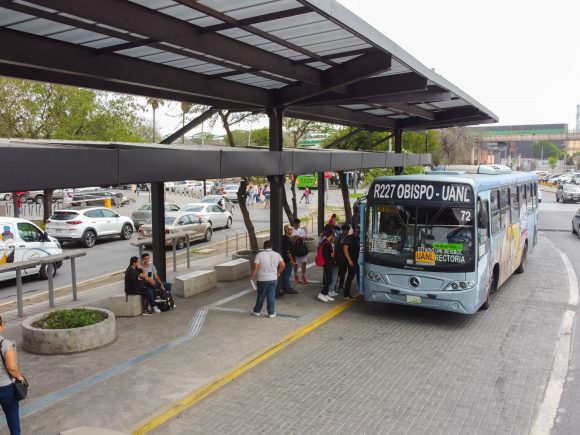
El programa de movilidad sustentable de la Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León tiene como estrategia central la promoción del transporte público colectivo, especialmente el sistema de transporte eléctrico metropolitano (metro), reconocido por su eficiencia y bajo impacto ambiental.
Para ampliar la cobertura hacia zonas no conectadas directamente por el metro, se fomenta el uso de rutas concesionadas de autobuses urbanos, con trayectos radiales, periféricos y locales que facilitan la accesibilidad a los diferentes campus. También se incluyen autobuses foráneos, que atienden a estudiantes de municipios cercanos, y el transporte público de alquiler, como taxis y vehículos de plataformas digitales (Uber, DiDi, Cabify, Beat, entre otras), que complementan la red de acceso.
En coordinación con las autoridades locales de transporte, se han optimizado las rutas de autobuses que llegan a los campus, alcanzando más de 40 recorridos que alimentan los alrededores de Ciudad Universitaria y mejoran la frecuencia, cobertura y accesibilidad para la comunidad universitaria.
Las rutas de transporte público urbano movilizan al año alrededor de 8 millones de personas que estudian o trabajan en el campus de Ciudad Universitaria.
- R-Álamo Santiago – Directo UANL
- R-Auto Transportes Azules y Amarillos
General Terán – Monterrey – UANL - R-Interenlace Directo Cadereyta – UANL
- R-1 Sector 1 San Nicolás – Tecnológico – Central – Las Puentes
- R-1 Sector 1 San Nicolás – Tecnológico – Directo – Pabellón
- R-1 Sector 4 Pilares – Central de Autobuses
- R-16/316 La Unidad – UANL
- R-17 Auditorio San Pedro – UANL
- 9. R-17 Pio X – UANL
- R-17 Santuario – UANL
- R-88 Cosmópolis – Jardines
- R-88 Cosmópolis – Moisés Sáenz
- R-101 Ébanos
- R-101 Manantial
- R-134 Fresnos – Puentes – 15 de Mayo
- R-134 Telmex – Metroplex – 15 de Mayo
- R-207 Penitenciaria
- R-209 Escobedo – Punta de Loma – Bosques
- R-209 Escobedo – Punta de Loma – Renacimiento – Olivos
- R-209 Exprés Escobedo – Hidalgo
- R-213 Cosmópolis – UANL
- R-213 Directa – UANL
- R-213 Quintas – UANL
- R-219 Sector 1 Tréboles – UANL – B. Reyes
- R-220 Pedregal
- R-220 Provileon
28. R-226 Sector 3 – Buena Vista – Joyas – Alameda
29. R-227 Clouthier – 16 de Septiembre
30. R-227 Clouthier – Constitución
31. R-227 Emiliano – 16 de Septiembre
32. R-227 Emiliano – Constitución
33. R-229 Ébanos – Metroplex – Mercado. Juárez
34. R-229 Robles – Metroplex – Mercado Juárez
35. R-232 La Unidad
36. R-232 La Unidad – San Marcos
37. R-316 Libramiento – Paraje San José
38. R-320 Fresnos – Puentes – Colón
39. R-685 Sector 1 Salinas Directo 213 40. R-685 Sector 2 Bosques de los Nogales

De manera paralela, se impulsa la incorporación de sistemas de movilidad no motorizada y eléctrica, como bicicletas, patines eléctricos y transporte ligero de nueva generación. Para facilitar su adopción, se han desarrollado ciclovías, estaciones de resguardo y espacios de circulación interna en los campus. Estas medidas generan beneficios ambientales, económicos y de salud, al tiempo que promueven un cambio cultural hacia formas de desplazamiento más sustentable, contribuyendo a reducir el uso del automóvil particular y a mejorar la movilidad urbana.
El programa de movilidad sustentable de la UANL constituye un esfuerzo integral orientado a transformar la cultura de desplazamiento en la comunidad universitaria. Al combinar la promoción del transporte público, el fortalecimiento de la movilidad no motorizada, la operación del TigreBus y la adopción de principios internacionales como la Pirámide Invertida de la Movilidad, la UANL no solo responde a los desafíos ambientales y de movilidad de la Zona Metropolitana de Monterrey, sino que además se posiciona como referente institucional en la construcción de entornos urbanos más equitativos y sustentables.
El sistema de transporte colectivo eléctrico conocido como Metro moviliza al año a más de 3.5 millones personas que estudian o trabajan en el campus de Ciudad Universitaria
Diariamente transitan por las áreas peatonales del campus de Ciudad Universitaria más de 80,000 personas
Objetivos específicos
- Conectar el interior de los campus con el contexto inmediato, dando prioridad a la movilidad peatonal segura.
- Encourage the use of non-motorized transportation on campus to improve mobility.
- Desincentivar el uso del automóvil mediante la reorganización de los espacios destinados a estacionamiento.
- Generar convenios de colaboración para vincular de forma eficiente con actores clave, entre ellos: Municipios y Dependencias Estatales.
Políticas
- Se priorizarán programas y proyectos que favorezcan el uso de medios de movilidad no motorizada y la seguridad e integridad del peatón.
- Se fomentará la movilidad no motorizada dentro de los campus
- Se implementarán conexiones entre dependencias, así como alternativas para fomentar el uso y desplazamiento de movilidad no motorizada
- Se promoverá la eficiencia y seguridad de los sistemas de transporte colectivo internos.
- Se impulsarán proyectos para la reorganización y mejora de las vías de circulación vehicular.
- Se fomentará la accesibilidad entre los espacios y edificios del campus, así como con el contexto inmediato externo
Ordering
- Planeación e implementación de un sistema de soporte para la movilidad no motorizada en los alrededores en campus.
- Coordinar las acciones entre dependencias y facultades relativas a la planeación, eliminación y mejora de barreras físicas que impiden el libre desplazamiento entre espacios y edificios.
- Coordinar con el transporte urbano externo la planeación, programación horaria y seguridad de sus rutas urbanas.
- Desarrollar acciones de mejora urbana en los accesos a los campus, para regular la entrada y salida de medios de movilidad motorizados.
Planeación
- Promover la mejora de vías, andadores y cruces peatonales para facilitar los desplazamientos de medios no motorizados en campus
- Promote non-motorized and zero-carbon mobility.
- Promover la reorganización de espacios destinados a dar servicio a medios motorizados.
- Gestionar el retiro de obstáculos, elementos y/o barreras que pongan en riesgo la movilidad no motorizada de manera segura, así como la accesibilidad universal.





